Binary code, the fundamental language of computers, may seem like a cryptic mystery at first glance. It's essentially a system relying on just two digits: 0 and 1. These digits represent electronic signals that can be on/off. By arranging these 0s and 1s in specific patterns, we can represent all kinds of information, from simple text to complex algorithms.
- Let's delve into the world of binary and explore how to interpret it step by step.
First, it's crucial to recognize that each position in a binary sequence, called a bit, holds a unique value. Starting from the rightmost digit, each bit stands for a power of 2. So, the rightmost bit is 20, the next one is 21, and so on.
Comprehending Binary to Decimal Conversion: The Fundamentals
Binary digits represent data using only two representations: 0 and 1. Conversely, the decimal system we use every day functions on ten digits. To transform a binary number into its decimal equivalent, you need to perform a series of calculations. Each binary digit location has a corresponding power of 2. You multiply each binary value by its corresponding power of 2 and then add the results to obtain the decimal equivalent.
- For example
- A binary sequence "1011"
- equals the decimal number 11.
The realm of computer science hinges on the fundamental language of binary. Computers operate by interpreting sequences of bits, represented as 0s and ones. However, human understanding stems on a more comprehensible form of communication: text. This is where binary translation comes into play, serving as the crucial bridge between these two worlds.
Binary translation involves the transformation of raw binary code into human-readable text. Sophisticated algorithms decipher the structures within binary data and decode them into meaningful words, sentences, and paragraphs. This process is fundamental to our interaction with digital information. From browsing the web to using applications and even accessing this very article, binary translation enables us to navigate the vast digital landscape.
- Algorithms employed in binary translation can range from simple character encoding schemes to complex natural language processing techniques.
- The choice of a suitable translation method depends on the nature of the binary data being processed.
Unveiling the Secrets of Binary Code
Binary code, the fundamental language of computers, appears as a sequence of 0s and ones. This seemingly simple framework contains the heart of all digital information. Each character represents a choice, either true or false, which when assembled in specific arrangements yields a rich tapestry of data that powers our contemporary world. From the applications we use daily to the sophisticated algorithms propelling artificial intelligence, binary code forms the foundation it all.
Interpreting of Deciphering Binary Messages
Binary code, the foundation of computers, can seem like a mysterious puzzle at first glance. However, with a little understanding of its principles, anyone can learn to decode these digital messages. A key aspect of this process is learning the meaning of each symbol. These simple digits, when arranged in combinations, form a vast range of information.
- Comprehending the binary system is like learning a new language.
- With practice, you can successfully translate even complex binary messages.
- Guides are abundant online and offline to support your learning journey.
Decoding Binary Worlds: Insights from Translation Tools
Binary translation tools are essential components in our ever-increasingly digital world. These sophisticated applications work by converting binary code, the language understood by computers, into human-readable formats. This transformation empowers us to analyze complex data sets, identify patterns, and ultimately gain valuable information from the vast amounts of information generated daily.
From troubleshooting software errors to uncovering encrypted messages, binary translation tools have a wide range of uses. They are also vital in fields like cybersecurity, where they help identify malicious code and protect sensitive data.
- Furthermore, binary translation tools can be used to
- simulate older computer systems, allowing developers to test their software on a variety of platforms.
- Lastly, the ability to interpret binary code is essential for anyone who wants to delve into the inner workings of computers and the digital world around us.
Switching Binary Numbers to English Words
Embarking on the journey of understanding binary numbers and their mapping into the realm of English words can be a intriguing endeavor. Binary, with its basis of 0s and 1s, represents a primary language for computers, while English words express the complexities of human communication. To harmonize this gap, we employ systematic procedures that map each binary string into its equivalent English word. This mechanism often involves breaking the binary number into units, each representing a specific character. By assigning these groups to their respective English counterparts, we can achieve this impressive feat.
Introduction to Binary Understanding
Binary code is the fundamental language of computers, representing data as sequences of binary digits. Comprehending binary interpretation allows you to delve into the core workings of how computers process information. Begin your journey by grasping the basics of how numbers are represented in binary form. Each digit in a binary sequence can hold only one of two values: 0 or 1. These values are then combined into sets to represent specific data.
A fundamental concept in binary interpretation is the place value system, similar to our decimal representation. In binary, each position represents a power of 2, initiating from the rightmost digit as 20. Moving to the left, each subsequent digit corresponds to a higher power of 2: 21, 22, and so on.
- As an example the binary number 1011. From right to left, each digit represents: 20 (1), 21 (0), 22 (1), and 23 (1).
- Summing the values of these places gives us: (1 x 20) + (0 x 21) + (1 x 22) + (1 x 23) = 1 + 0 + 4 + 8 = 13.
Consequently, the binary number 1011 represents the decimal number 13.
Dominating Digital Code
Embark on a journey through the realm of binary code, unlocking its secrets and transforming theoretical knowledge to practical applications. Journey through the fundamentals of bits and bytes, understanding their meaning in the digital landscape. Build a firm foundation by analyzing logic gates, Boolean algebra, and binary arithmetic, creating the groundwork for sophisticated programming concepts.
- Sharpen your ability to interpret human language to binary instructions, bridging the gap between abstract thought and concrete computational processes.
- Implement your newfound knowledge by constructing simple programs, testing with different algorithms, and experiencing the power of binary in action.
Consequently, mastery over binary empowers you to transcend into a skilled programmer, capable of creating innovative solutions and shaping the future of technology.
Demystifying Binary
Diving into the realm of binary conversion can seem daunting at first. But fear not! This fundamental idea is surprisingly straightforward, even for absolute beginners. At its core, binary uses just two digits, 0 and 1, to represent all data in a computer. Think of it like a secret language where each combination of 0s and 1s represents a letter, number, or even an entire image.
Whether you're learning about computer science for the first time or looking to deepen your technical understanding, mastering binary conversion is a valuable tool. It allows you to decode how computers actually function and gives you a glimpse into the very structure of digital technology.
- Understanding binary conversion opens doors to a world of possibilities, from creating your own software to diagnosing computer problems.
- With a firm grasp of this fundamental concept, you can engage with technology on a deeper level and recognize the potential of the digital world.
Unveiling the Power of Binary
Binary code, a fundamental language of computers, offers a powerful glimpse into the foundation of digital computation. By leveraging its simple structure of 0s and 1s, we gain access to a realm of infinite possibilities. This numerical system comprises the very fabric of our modern technological world, driving everything from basic calculations to complex artificial intelligence.
- Understanding binary unveils doors to a more profound appreciation of how technology functions.
- Utilizing this unique language enables individuals to engage in the ever-evolving field of computer science.
Grasping Binary: A Practical Approach
Translating binary code into its human-readable equivalent can seem daunting at first. Nonetheless, it's a fundamental skill for anyone interested in computing. Binary, the language of computers, is a simple system that uses only two digits: 0 and 1. Each digit represents an electronic state, on/off or high/low. By arranging these digits into sets, we can represent letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Suppose a simple example: the letter 'A' in binary is represented as 01000001. This sequence of 8 bits represents the character 'A'.
- Similarly, other characters and symbols have their own unique binary codings.
- To translate binary, we can use a number of methods, such as online converters or coding languages.
With practice, you'll be able to decode binary code with ease and gain a deeper understanding of how computers work.
Comprehending Binary Representation
Binary representation is the backbone of how computers manipulate information. It's a method that uses only two digits: 0 and 1. Each digit, known as a bit, can represent an true/false state. These bits are clustered into larger units called bytes, which contain data. Understanding binary representation is vital for programmers as it allows them to communicate directly with the hardware.
- Furthermore, binary representation is used in a wide spectrum of applications, including data transmission
- For example, the characters on your keyboard are converted into binary code before being displayed on your screen.
Decoding the Digital World: A Look at Binary
Computers don't communicate in the way humans do. They rely on a fundamental language called binary code. This system employs only two digits: 0 and 1. Each of these digits represents an digital state, either "on" or "off." Groups of these 0s and 1s form bits, which can then be structured into bytes to represent letters, numbers, and even detailed instructions.
While it may seem confusing at first, binary code is the foundation of all computer operations. By means of simple calculations involving 0s and 1s, computers can perform a vast range of tasks, from presenting images to processing complex software programs.
Binary Translation: Key Concepts and Techniques
Binary translation is a technique/method/process that involves converting machine code from one architecture to another without executing the original code. This transformation/conversion/mapping enables applications built for one platform to execute/run/function on a different architecture/hardware/system. It plays a crucial role in areas such as emulation/virtualization/cross-platform compatibility, allowing legacy software to operate on modern hardware and facilitating the development of portable applications.
- Core concepts in binary translation include disassembly/decompilation/code analysis, instruction rewriting/remapping/transformation, and platform-specific code generation/synthesis/output.
- Common techniques used in binary translation involve/employ/utilize static and dynamic analysis/interpretation/execution methods, along with techniques for optimizing the translated code for performance and efficiency.
Furthermore/Additionally/Moreover, various challenges arise in binary translation, such as handling platform-specific dependencies, preserving code semantics, and ensuring security and reliability.
From Bits to Meaning: The World of Binary Translation
Binary translation is the fascinating process of converting machine code from one architecture to another. At its core, it's about understanding the fundamental building blocks of computation—bits—into meaningful instructions that different processors can execute. This intricate symphony involves sophisticated algorithms and a deep understanding of both source and target architectures. Binary translators play a vital role in ensuring software portability, allowing applications to run on a wider range of devices, bridging the gap between different worlds of computing.
Decoding Digital Information: A Look at Binary Translation
Our contemporary world depends on a complex system of knowledge transfer. This transmission is fundamentally based on binary code, Translate from binary a language made up of only dual states: 0 and 1. Binary translation functions as the crucial bridge between this numerical representation and the meaningful content we communicate with daily.
Simply put, binary translation transforms human-readable information into a format comprehensible by electronic devices. This process requires sophisticated software that convert text, images, sound, and other data into their corresponding binary forms.
- Conversely, when receiving information, the opposite process occurs. Binary translation interprets the numerical sequence back into its original form, allowing us to access the intended content.
- Without this crucial translation process, our electronic world would be a collection of gibberish code, effectively useless.
Demystifying Binary Conversion: A User-Friendly Guide
Understanding binary code can seem intimidating at first, but it's fundamentally simpler than you might think. This detailed guide will walk you through the basics of binary conversion, equipping you with the knowledge to translate between decimal and binary numbers. We'll explore individual step in a clear and concise approach, making the process accessible even for beginners.
- We'll begin with understanding what binary code is and how it operates.
- , Following this, we'll learn the methodology involved in converting decimal numbers to binary.
- you'll be able to practice your newfound skills with examples.
Software Interpretation
Binary translation, also referred to as program emulation, is a technique used to execute machine code from one architecture on a target architecture. This involves analyzing the original binary code and generating equivalent instructions for the target system. Several applications utilize binary translation, including running legacy software on modern hardware, optimizing performance on heterogeneous systems, and supporting cross-platform code execution.
The process of binary translation typically involves several stages: disassembly of the source code, analysis of the control flow and data dependencies, generation of target instructions, and tuning of the translated code. Binary translators can be static in nature, depending on whether they analyze and transform the entire binary program beforehand or at runtime.
- Difficulties in binary translation include handling complex control structures, improving performance across diverse architectures, and addressing security concerns related to malicious code manipulation.
- Development in this field is ongoing, with a focus on improving the accuracy, efficiency, and portability of binary translators.
Translating Binary Information
Binary interpretation is a fundamental process in data analysis, involving the conversion of binary code into understandable formats. This conversion allows analysts to obtain meaning from raw binary data, which is often the core of digital information. Through various algorithms and techniques, binary interpretation exposes valuable insights that can guide decision-making processes in a wide range of fields.
 Alana "Honey Boo Boo" Thompson Then & Now!
Alana "Honey Boo Boo" Thompson Then & Now!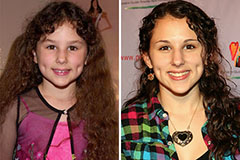 Hallie Eisenberg Then & Now!
Hallie Eisenberg Then & Now! Val Kilmer Then & Now!
Val Kilmer Then & Now! Jennifer Love Hewitt Then & Now!
Jennifer Love Hewitt Then & Now! Robbie Rist Then & Now!
Robbie Rist Then & Now!